[บริการวิชาการฯ] การสู้ด้วยคุณค่า Value proposition และ แผนภาพการสร้างคุณค่า (The Value Proposition Canvas)
บทความโดย : คณาจารย์วิชาเอกการจัดการธุรกิจไซเบอร์ วิทยาลัยนวัตกรรมสื่อสารสังคม
การสู้ด้วยคุณค่า Value proposition
ดร.ฉัตรเมือง เผ่ามานะเจริญ
ดร.เบญจวรรณ อารักษ์การุณ
อ.ทิพภาวรรณ พลล่องช้าง
แผนภาพการสร้างคุณค่า (The Value Proposition Canvas)
ดร.ฐิศิรักน์ โปตะวณิช
ผศ.ดร.ประมา ศาสตระรุจิ
ดร.วีระนันท์ คำนึงวุฒิ
อ.ทิพภาวรรณ พลล่องช้าง
การสู้ด้วยคุณค่า Value proposition
ปัจจุบัน เราอาจจะเห็นได้ว่าการแข่งขันในการทำธุรกิจยุคดิจิตัลอยู่ในระดับที่สูงมาก ยิ่งเกิดสถานการณ์ covid 19 แล้วนั้น จะเห็นได้ว่าคนเข้ามาใช้เครื่องมือการโฆษณาออนไลน์กันมากขึ้น ไม่ว่าจะเป็นการใช้สื่อโซเชี่ยลต่างๆ หรือแพลตฟอร์มมาร์เก็ทเพลส อย่าง lazada shopee เพราะสะดวก และใช้เงินในการตลาดน้อยกว่า จึงทำให้เป็นที่นิยมในธุรกิจใหม่ๆเป็นที่รู้จักได้อย่างรวดเร็ว
แต่เราจะเห็นได้ว่าธุรกิจใหม่ๆนั้นเกิดขึ้นแบบก้าวกระโดดและล้มแหลวในช่วงเวลาอันสั้นเช่นกัน เพราะเมื่อเราเข้าถึงตลาดได้ง่าย คนอื่นก็ทำได้เช่นเดียวกัน จนโดนคู่แข่งแซงหน้าไป สิ่งที่มักผิดพลาดกันหลักๆคือ เรื่องการนำเสนอสินค้าและบริการได้ ไม่ ตรงตามความต้องการของลูกค้าอย่างแท้จริง
ประเด็นหลักที่สามารถตอบโจทย์ในการดำเนินธุรกิจยุคดิจิตัล คือ การทำอย่างไรให้ธุรกิจที่เราสร้างขึ้นมานั้นแตกต่างจากคู่แข่ง และอยู่รอดอย่างยั่งยืน ซึ่งก็คือการออกแบบคุณค่าที่เหนือกว่าคู่แข่งได้อย่างไร ในขณะที่สินค้าและบริการต่างๆแทบจะคล้ายกันไปหมด
คีย์หลักของชะตาชีวิตธุรกิจคือ สินค้าหรือบริการที่ส่งมอบให้ลูกค้านั้นตรงตามความต้องการและสามารถแก้ไขปัญหาของลูกค้าได้จริง ที่สำคัญต้องมีตลาดลูกค้าที่รองรับสิ่งเหล่านั้นอยู่จริงๆ

(ภาพโดย Ronald Carreño จาก Pixabay)
คุณค่าที่เหนือกว่าคู่แข่ง (Value proposition) คืออะไร
Value proposition แปลตรงตัวว่า “คุณค่าที่ส่งมอบให้ลูกค้า”
เมื่อธุรกิจของคุณ มีสินค้าหรือบริการที่คล้ายกับคู่แข่ง หรือแตกต่างกันน้อยมาก เราก็จะต้องเพิ่มว่าเราจะมอบคุณค่าให้กับลูกค้าเป็นอะไรได้บ้าง เช่น ประโยชน์ต่างๆ ประสบการณ์ที่ไม่เหมือนใคร ความรู้สึกที่แตกต่างเมื่อใช้สินค้าและบริการ
ตัวอย่างที่เห็นได้ชัด คือ ร้านกาแฟ Starbucks คีย์ที่ทำให้ประสบความสำเร็จไม่ได้อยู่ที่กาแฟ แต่เป็น ประสบการณ์ดีๆที่ลูกค้าได้รับผ่านพนักงาน สถานที่ และบรรยากาศภายในร้าน ซึ่งคุณค่าที่ลูกค้าได้รับก็คือ การเป็นสถานที่ดื่มกาแฟที่ลูกค้าสามารถไว้ใช้คุยงานได้ และทำให้ลูกค้าดูดีเมื่อนั่งอยู่ในร้านหรือถือแก้วสตาร์บัคส์ออกไปจากร้านก็ตาม
ธุรกิจที่มีคุณค่าเหนือกว่าคู่แข่งชัดเจน จะทำให้ลูกค้าแน่ใจในการเลือกใช้สินค้าและบริการมากกว่าคู่แข่ง ซึ่งอาจะเป็น การคิดค้นนวัตกรรมใหม่ๆแทนที่ หรือเพิ่มเติมคุณสมบัติหรือคุณักษณะใหม่ๆ (Features and Attributes) เข้าไป
สิ่งสำคัญ อย่าลืมว่า คุณค่านั้นต้องเน้นการแก้ไขปัญหาหรือตอบสนองความต้องการของลูกค้ากลุ่มเป้าหมาย ซึ่งอาจเป็น เชิงปริมาณ เช่น ราคา หรือความรวดเร็วในการจัดส่ง และ คุณค่าเชิงคุณภาพ เช่นการออกแบบ หรือ การสร้างประสบการณ์
ประเภทของคุณค่า สามารถแบ่งหลักๆ ได้ดังนี้
- สิ่งใหม่ / การเป็นครั้งแรก / ความไม่คุ้นเคย
การมอบความต้องการใหม่ๆ หรือสิ่งใหม่ๆ ที่ลูกค้าไม่เคยรับรู้มาก่อน เพราะยังไม่เคยมีสินค้าหรอบริการนี้มาก่อน ส่วนใหญ่จะเป็นสินค้าที่เกี่ยวกับเทคโนโลยีหรือนวัตกรรม
- ประสิทธิภาพ
การเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพของสินค้าและบริการให้ดีขึ้น ซึ่งเป็นพื้นฐานที่ใช้กันทั่วไป เช่น ธุรกิจคอมฯ ก็จะมีการนำเสนอความจุที่มากขึ้น หรือกราฟฟิคที่ดีขึ้น แต่ข้อจำกัดของคุณค่านี้คือ ในบางครั้งการพัฒนาประสิทธิภาพจะตามไม่ทันความต้องการของลูกค้าที่มากขึ้นแบบก้าวกระโดด
- Customization การปรับแต่งได้
การที่ลูกค้าสามารถปรับแต่งสินค้าหรือบริการให้ได้ตามความต้องการ ก็ถือว่าเป็นการสร้างคุณค่าที่เหนือกว่าคู่แข่งได้เช่นกัน เมื่อลูกค้าสามารถปรับแต่งสินค้าและบริการได้นั้นจะทำให้ลูกค้ารู้สึกถึงความเป็นเจ้าของ ทำให้เกิดความรู้สึกเป็นส่วนหนึ่งและจงรักพักดีกับแบรนด์มากยิ่งขึ้น
- Getting the job done ทำให้งานลูกค้าสำเร็จ
สินค้าหรือบริการที่มอบคุณค่าด้วยการช่วยงานบางอย่างให้สำเร็จง่ายขึ้น เช่น Grab Food ที่ช่วยให้ลูกค้าไม่ต้องออกไปซื้ออาหารและต่อคิวในช่วงสถานการณ์โควิด-19 ลดภาระเรื่องการออกไปซื้ออาหารช่วงกักตัวให้ลูกค้าได้
- Design การออกแบบ
การออกแบบที่โดดเด่นกว่าคู่แข่งท่ามกลางสินค้าหรือการบริการที่คล้ายกัน ก็ถือว่าเป็นการสร้างคุณค่าที่สำคัญของธุรกิจประเภทแฟชั่น
- Price ราคา
การใช้กลยุทธ์ราคาต่ำกว่าคู่แข่งนั้นใช้ได้สำหรับกลุ่มลูกค้าที่มีความอ่อนไหวต่อราคาเท่านั้น และต้องมั่นใจด้วยว่าต้นทุนการดำเนินธุรกิจตนเองนั้นต่ำเช่นกัน บางครั้งก็อาจนำมาปรับเป็นการทำโปรโมชั่นของฟรี เช่น โค้ดส่วนลดฟรี ผลิตภัณฑ์ทดลองฟรี เป็นต้น
- Cost reduction การลดต้นทุน
การช่วยลูกค้าลดต้นทุนหรือค่าใช้จ่ายก็ถือเป็นการสร้างคุณค่าที่เหนือกว่าคู่แข่งอีกประเภทหนึ่ง เช่น ลาซาด้า Lazada ช่วยให้ลูกค้าเป็นเจ้าของธุรกิจโดยประหยัดต้นทุนในการสร้างเว็บไซต์ร้านค้าของตนเอง
- Risk reduction การลดความเสี่ยง
การสามารถช่วยลูกค้าลดหรือบรรเทาความเสี่ยงในการใช้สินค้าและบริการก็สามารถเพิ่มคุณค่า ให้เหนือกว่าคู่แข่งได้ เช่น การรับประกันคุณภาพภายในหนึ่งปี หรือ บริการหลังการขายของสินค้าและบริการนั้นๆ เป็นต้น
- Accessibility ความสามารถในการเข้าถึง
การช่วยให้ลูกค้าสามารถเข้าถึงสินค้าและบริการได้ง่ายขึ้น ซึ่งอาจเกิดมาจากธุรกิจที่มีเทคโนโลยีหรือนวัตกรรมเข้ามาใช้ เช่น ประกันในรูปแบบ unit link ที่ทำให้ลูกค้าสามารถเข้าถึงการลงทุนในประกันควบคู่กับการลงทุนกองทุนที่หลากหลายมากขึ้น
- Convenient / Usability ความสะดวกสบายในการใช้งาน
การทำให้บางสิ่งหรือการทำกิจกรรมบางอย่างสะดวกง่ายขึ้ เช่น ไอพอดและ iTunes ทำให้ลูกค้าสามารถ ค้นหาเพลง ดาวน์โหลดเพลง และฟังเพลงในรูปแบบดิจิตอลได้ง่ายขึ้น
จากรูปแบบที่กล่าวมาทั้งหมดจะเห็นได้ว่า การนำเสนอสินค้าและบริการที่ไปช่วยแก้ปัญหาลูกค้าได้และในขณะเดียวกันก็สามารถช่วยให้ลูกค้ามีชีวิตที่ดีขึ้น ได้นั้น เป็นการสร้างคุณค่าที่เหนือกว่าคู่แข่ง ที่เปรียบเสมือนการแก้ Pain Point (จุดเจ็บปวด) หรือปัญหาของลูกค้าได้อย่างตรงจุด แต่กว่าจะถึงจุดนั้นต้องสามารถวิเคราะห์ให้ได้ว่า Pain point (จุดเจ็บปวด) หรือ ปัญหาที่แท้จริงของลูกค้านั้นคืออะไร แล้วรักษาให้ดีขึ้น (Gain) อย่างไร
แผนภาพการสร้างคุณค่า (The Value Proposition Canvas)
ก่อนอื่นต้องทำความเข้าใจก่อนว่า แผนภาพการสร้างคุณค่า (The Value Propositions Canvas) นี้เป็นเครื่องมือที่ช่วยในการออกแบบการสร้างคุณค่าของสินค้าและบริการของคุณให้ตรงตามความต้องการของลูกค้า หรือสามารถแก้ปัญหาของลูกค้าให้ได้ตรงจุด เพื่อสร้างคุณค่าที่เหนือกว่าคู่แข่ง
แบ่งออกเป็น 2 ส่วนด้วยกันคือ
- ส่วนของลูกค้า (Customer Profile) ช่วยในการทำความเข้าใจลูกค้า
- ส่วนของคุณค่าที่นำเสนอ (Value Map) ส่วนของคุณค่าที่นำเสนอ
ซึ่งการเริ่มต้นคิดธุรกิจหรือการออกแบบคุณค่านั้นจำเป็นต้องมองการออกแบบสินค้าและบริการ ที่ลูกค้าเป็นหลัก แล้วค่อยตามด้วยคุณค่าที่จะนำเสนอ
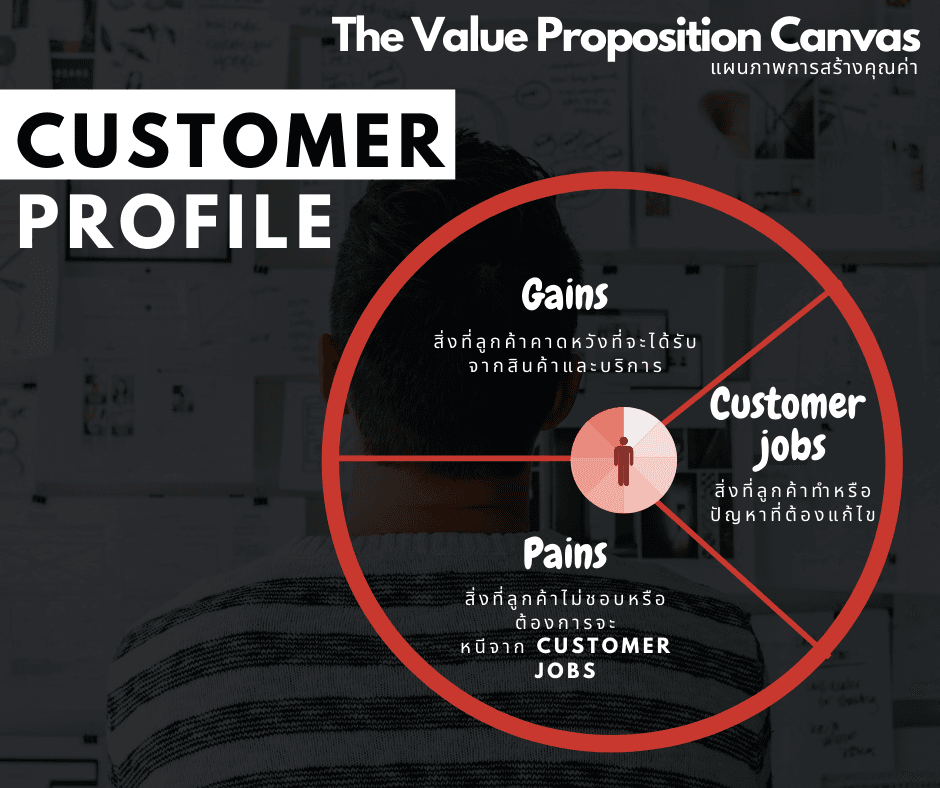
แผนภาพการสร้างคุณค่า: ส่วนของลูกค้า (Customer Profile)
(Osterwalder et al., 2014) (ภาพโดย Pexels จาก Pixabay)
ส่วนของลูกค้า (Customer Profile)
ส่วนนี้จะเป็นการทำความเข้าใจความต้องการที่แท้จริงของลูกค้าที่เป็นกลุ่มเป้าหมาย โดยการมองให้ลึก 3 ประเด็น
- Customer jobs (งานที่ลูกค้าต้องทำ) คือ เบื้องหลังในการทำสิ่งใดสิ่งหนึ่ง หรือการทำงาน (Job) รวมไปถึงสิ่งที่ลูกค้าทำหรือปัญหาที่ต้องแก้ และมีความต้องการอะไรบางอย่างมาช่วย ทั้งในส่วนของผลที่จับต้องได้และผลทางอารมณ์/ความรู้สึกที่จับต้องไม่ได้ แบ่งเป็น 4 ประเภท
- งานตามหน้าที่ (Functional jobs) สิ่งที่อยากทำให้สำเร็จ/ปัญหาเฉพาที่ต้องการแก้ไข เช่น อยากรักษาหุ่น/กินอาหารที่มีประโยชน์ ม ต้องการประประหยัดเวลาในการทำงานบ้าน เป็นต้น
- งานทางสังคม (Social jobs) เกิดตอนที่ลูกค้าอยากดูดี / ยกสถานะทางอำนาจและสังคม ซึ่งเกี่ยวกับงานที่ลูกค้าอยากให้คนอื่นมองแบบที่ตัวเองต้องการ เช่น อยากให้คนอื่นมองว่าเราเป็นคนประสบความสำเร็จ หรือ อยากดูเป็นแฟชั่นนิสต้า (Fashionista) ในสายตาผู้อื่น เป็นต้น
- งานส่วนบุคคล (Personal/emotional jobs) งานที่เกี่ยวข้องกับอารมณ์ที่ลูกค้าต้องการได้รับเช่น อยากรู้สึกดี หรือ อยากรู้สึกมั่นคง เป็นต้น
- งานสนับสนุน (Supporting jobs) งานที่สนับสนุนบางสิ่งให้ง่ายขึ้น บางครั้งจะเป็นงานที่สนับสนุนที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการซื้อสินค้าและบริการได้เช่นกัน เช่น การเปรียบเทียบราคาหรือคุณภาพของสินค้า การรีวิวหรือให้ข้อแนะนำเกี่ยวกับสินค้าและบริการ การนำสินค้ไปขายต่อ เป็นต้น
1.2 Pains (ความยุ่งยากลำบากที่ลูกค้ามักพบเจอ) คือ การระบุสิ่งที่ลูกค้าไม่ชอบหรือต้องการจะ
หลีกหนีจากสิ่งที่ลูกค้าต้องทำ (Customer jobs) อาจเกิดได้จากที่ตัวสินค้าและบริการ ไปจนถึงความกลัว หรือความเชื่อผิดๆที่มีต่อสินค้าและบริการ ซึ่งจะเป็นสิ่งที่ลูกค้าไม่ต้องการ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นก่อน ระหว่าง และหลังทำสิ่งนั้นๆ แบ่งเป็น 3 ประเภท
- ผลลัพธ์ไม่เป็นไปตามที่ปรารถนา (Undesired outcome) สามารถเป็นได้ในเชิงผลลัพธ์ (เช่น สินค้าหรือบริการไม่มีประสิทธิภาพพอ หรือการทำสิ่งนี้อาจมีผลร้ายข้างเคียง) เชิงสังคม (เช่น ทำสิ่งนี้แล้วทำให้ลูกค้าดูแย่) เชิงอารมณ์ (เช่น ลูกค้ารู้สึกแย่ทุกครั้งที่ทำสิ่งนี้) ตัวอย่างเช่น การไปยิมเป็นเรื่องน่าเบื่อ หรือสินค้ามีรูปลักษณ์ที่ไม่สวย เป็นต้น
- อุปสรรค (Obstacles) หรือสิ่งที่ทำให้ขวางไม่ให้ลูกค้าทำงานบางอย่างได้สำเร็จหรือทำให้งานล่าช้า เช่น การไม่มีเวลาออกกำลังกาย หรือไม่มีเงินพอจะจ้างเทรนเนอร์ส่วนตัว เป็นต้น
- ความเสี่ยง (Risk) หรือการที่บางอย่างอาจไม่เป็นไปตามที่ควรหรือเกิดผลลัพธ์ในเชิงลบ เช่น ลูกค้าอาจเสียภาพลักษณ์ถ้าใช้สินค้านั้นๆ เป็นต้น
1.3 Gains (สิ่งที่ลูกค้าคาดหวังจะได้รับเพิ่มเติม) เป็นส่วนที่ต่อกับ Customer jobs เป็นสิ่งที่ลูกค้าคาดหวังที่จะได้รับจากสินค้าและบริการ รวมไปถึงความต้องการเพิ่มเสริมจากสิ่งที่มีอยู่ทำให้ลูกค้าเกิดความประทับใจ ได้แก่ อรรถประโยชน์ (Functional utility) การยอมรับจากสังคม (Social gain) ความรู้สึกที่ดี (Positive emotion) และ การประหยัด (Cost saving) ซึ่งจะมีทั้งเป็นไปตามที่คาดหวังหรือเกินความคาดหวัง แบ่งเป็น 4 ประเภท
- Required Gain (สิ่งที่ได้รับที่จำเป็นต้องมี) เป็นความคาดหวังโดยทั่วไปที่สินค้าและบริการนั้นๆควรจะมี เช่น สมาร์ทโฟนจำเป็นที่จะต้องสามารถใช้เล่นอินเทอร์เน็ต เป็นต้น
- Expected Gain (สิ่งทีได้รับตามที่คาดหวังไว้) เป็น ความคาดหวังทั่วไปที่ลูกค้าคาดว่าจะได้รับจากสินค้าและบริการนั้นๆ เช่น ลูกค้าคาดหวังว่า iPhone จะต้องมีรูปแบบลักษณ์และการออกแบบที่ดูดี
- Desired Gain (สิ่งได้รับตามที่ปรารถนา) เป็นสิ่งทีได้รับเกินไปกว่าความคาดหวังโดยทั่วไป หรือเป็นสิ่งที่ลูกค้าคาดหวังเพิ่มเติมจากสิ่งที่มีอยู่ โดยสามารถสอบถามลูกค้าถึงความต้องการนี้ได้ เช่น ลูกค้าอยากให้สมาร์ทโฟนเชื่อมต่อกับอุปกรณ์อื่น ๆที่มีอยู่แล้ว เป็นต้น
- Unexpected Gain (สิ่งทีได้รับเกินกว่าที่คาดหวังไว้) โดยเป็นสิ่งที่ลูกค้าไม่เคยคาดหวังมาก่อน หรือถ้าถามลูกค้าก็ไม่สามารถให้คำตอบนี้ได้ เช่น ลูกค้าไม่เคยคาดหวังว่าโทรศัพท์มือถือจะมีระบบสัมผัสหน้าจอ (Touch screen) จนกระทั่ง iPhone ได้เกิดขึ้น
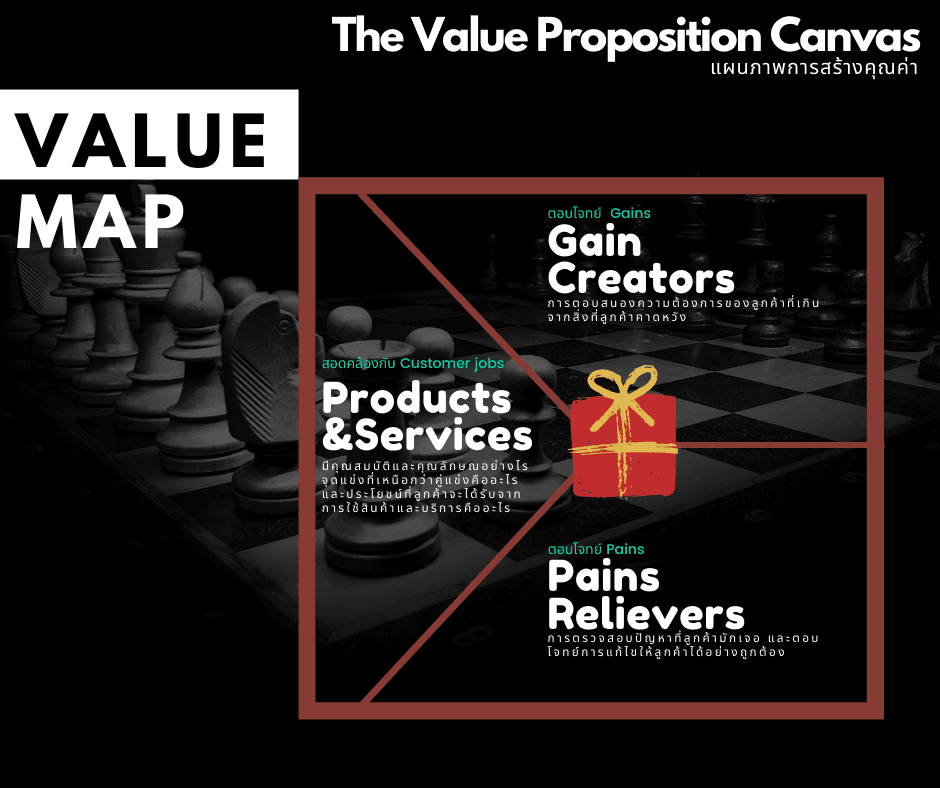
แผนภาพการสร้างคุณค่า: ส่วนของคุณค่าที่นำเสนอ (Value Map)
(Osterwalder et al., 2014) (ภาพโดย FelixMittermeier จาก Pixabay)
ส่วนของคุณค่าที่นำเสนอ (Value Map)
ส่วนนี้จะเป็นแผนภาพที่ช่วยให้ธุรกิจสามารถออกแบบสินค้าและบริการให้มีคุณค่าต่อลูกค้า และจะสามารถเข้าไปอยู่ในใจลูกค้าและสนองความต้องการของลูกค้าได้ แบ่งออกเป็น 3 ประเด็นหลัก
2.1. Products and Services (สินค้าหรือบริการที่ตอบโจทย์ความต้องการพื้นฐาน) เป็นการสรุปว่าสินค้าและบริการนั้นควรมีคุณสมบัติและคุณลักษณะอย่างไร จุดแข่งที่เหนือกว่าคู่แข่งคืออะไร และประโยชน์ที่ลูกค้าจะได้รับจากการใช้สินค้าและบริการคืออะไร โดยต้องสอดคล้องกับ Customer jobs ในส่วนของ Customer Profile ซึ่งวัตถุประสงค์ต้องมีชัดเจนว่าผลิตมาเพื่ออะไร แบ่งออกเป็น 4 ประเภท
- Physical/ Tangible (ประเภทที่สามารถจับต้องได้) เช่น สินค้าที่ผลิตจากโรงงาน เป็นต้น
- Intangible (ประเภทที่ไม่สามารถจับต้องได้) เช่น ลิขสิทธิ์ หรือการให้บริการหลังการขาย เป็นต้น
- Digital (ประเภทที่เกี่ยวกับดิจิตอล) เช่น การดาวน์โหลดเพลง หรือบริการการเก็บข้อมูลในออนไลน์ เป็นต้น
- Financial (ประเภทที่เกี่ยวกับการเงิน) เช่นการลงทุนในกองทุน หรือประกันชีวิต เป็นต้น
2.2 Pains Relievers (ความสามารถในการผ่อนคลายความทุกข์ที่ลูกค้ามี) เป็นส่วนที่ไปตอบโจทย์ Pains (ความลำบากที่ลูกค้ามักเจอ) ใน Customer Profile ซึ่งคุณจะต้องพิจารณาและสำรวจตรวจสอบปัญหานั้นให้ถี่ถ้วน เพราะหากสินค้าและบริการสามารถแก้ไขปัญหาในเรื่องนั้นได้ถูกต้อง ก็จะสามารถลดความยุ่งยากของลูกค้าลงได้อย่างมาก ถ้าลูกค้ายังพบว่ามีความยากลำบากอยู่ การที่ธุรกิจสามารถไปเติมเต็มช่องว่างเหล่านั้นได้ ก็เหมือนกับการให้ยาที่ถูกต้อง เพราะสามารถตอบโจทย์ตรงนี้โดยการลบล้าง หลีกหนี หรือแก้ไขสิ่งที่ลูกค้าไม่ชอบได้หมดทุกข้อ
2.3 Gain Creators (ความสามารถในการสร้างสรรค์ประโยชน์ใหม่ๆให้แก่ลูกค้า) เป็นการตอบสนองความต้องการแบบเหนือความคาดหมาย โดยส่วนนี้จะไปตอบโจทย์ Gains ของ Customer Profile หากคุณสามารถออกแบบคุณค่าเสริมที่เพิ่มเติมหรือเกินจากสิ่งที่ลูกค้าคาดหวัง จะช่วยสร้างข้อได้เปรียบทางการแข่งขัน เกิดความโดดเด่นจนคู่แข่งไม่สามารถตามทันได้
เมื่อทำการระบุแผนภาพทั้ง 2 ฝั่งได้แล้ว จะทำให้เกิดการสร้างคุณค่าของสินค้าและบริการที่เหมาะสมตรงจุด (Fit) และเหนือกว่าคู่แข่งได้นั่นเอง
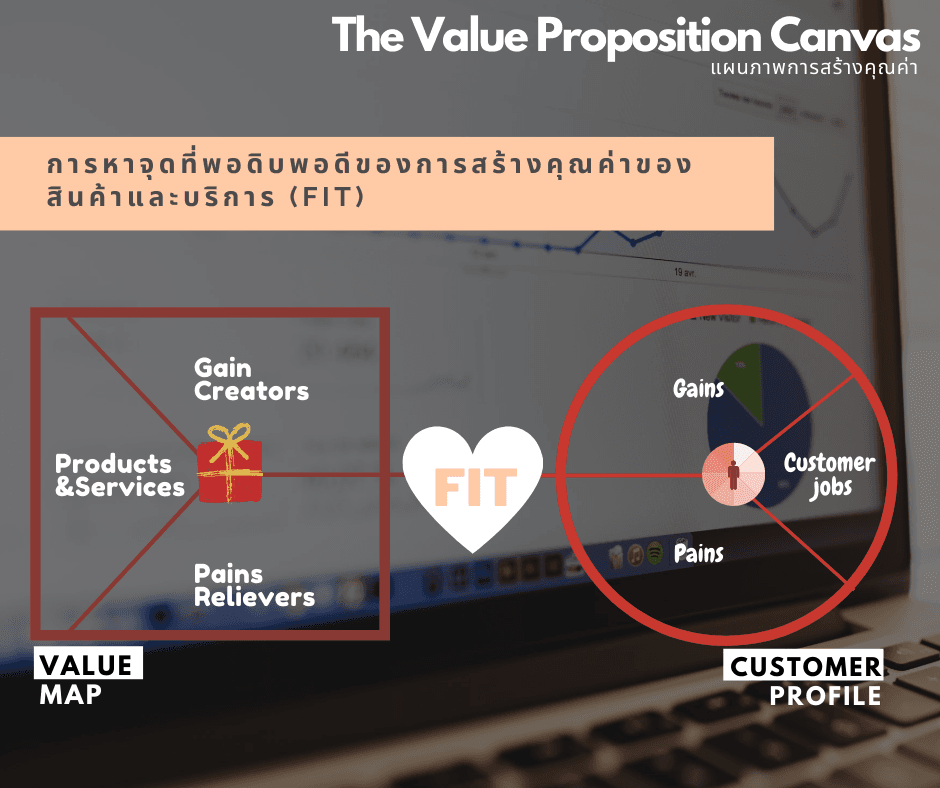
แผนภาพการสร้างคุณค่า: การสร้างคุณค่าของสินค้าและบริการที่เหมาะสมตรงจุด (Fit)
(Osterwalder et al., 2014) (ภาพโดย Lalmch จาก Pixabay)
สรุป
การออกแบบคุณค่าที่เหนือกว่าคู่แข่งได้นั้น คือ การหาจุดที่พอดิบพอดีของการสร้างคุณค่าของสินค้าและบริการ โดยจะต้องสามารถตอบโจทย์ทั้งในเรื่องของการแก้ไขความยุ่งยากลำบากที่ลูกค้ามักพบเจอ (Pains) และ การนำเสนอสิ่งที่ลูกค้าคาดหวังจะได้รับเพิ่มเติม (Gains) มี 3 ขั้นตอนคือ
- การทำให้สินค้าและบริการแก้ปัญหาได้ถูกจุด หรือ ตรงตามความต้องการของตลาด (Problem-Solution Fit)
สิ่งนี้จะได้มาจากการสังเกตและการหาข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับความยุ่งยากลำบากที่ลูกค้ามักพบเจอ (Pains) และ การนำเสนอสิ่งที่ลูกค้าคาดหวังจะได้รับเพิ่มเติม (Gains) ที่เกี่ยวข้องที่สุดกับกลุ่มเป้าหมาย โดยที่อาจจะยังไม่ต้องหาหลักฐานมาสนับสนุน แต่ให้พยายามระบุข้อมูลหรือคำตอบให้ตรงกับกลุ่มเป้าหมายให้ได้มากที่สุด
- การทำให้ลูกค้าเห็นสินค้าและบริการของเราแล้วอยากได้ คือ ถูกดึงดูดให้ซื้อ (Product-Market Fit)
ขั้นตอนนี้คุณจำเป็นต้องทดสอบตลาดจริงเพื่อดูว่าสินค้าและบริการต้องสามารถตอบโจทย์ความต้องการพื้นฐาน (Products and Services) ผ่อนคลายความทุกข์ยากที่ลูกค้ามี (Pains Relievers) และ สร้างสรรค์ประโยชน์ใหม่ๆให้แก่ลูกค้า (Gain Creators) ได้จริง ซึ่งในขั้นตอนนี้เป็นการทดสอบว่าคุณค่าของสินค้าและบริการที่ออกแบบมานั้นทำได้จริงหรือเปล่า ในบางครั้ง ลูกค้าอาจไม่ให้ความสนใจเลยด้วยซ้ำ ดังนั้นในขั้นตอนนี้จึงเป็นขั้นตอนที่ใช้เวลาและอาจจะต้องย้อนทำระหว่างขั้นตอนที่ 1 และขั้นตอนที่ 2
- การทำให้สินค้าและบริการเกิดผลประกอบทางการเงินที่เป็นกำไรและเติบโต (Business Model Fit)
ขั้นตอนนี้คือการยืนยันว่า ธุรกิจที่มีคุณค่าที่เหนือกว่าคู่แข่งได้นั้นจะต้องนำไปสู่ความสำเร็จโดยจะต้องมีผลประกอบการทางการเงินที่มีกำไรและเติบโตอย่างต่อเนื่อง ซึ่งในการทำธุรกิจนั้น นอกจากจะสามารถส่งมอบคุณค่าที่เหนือกว่าคู่แข่งไปยังลูกค้าได้แล้ว ยังจะต้องมีความสามารถในการออกแบบโมเดลธุรกิจ (Business Model) ที่เหมาะสมไปด้วย โดยจะต้องคำนึงถึงองค์ประกอบอื่นที่จะช่วยสร้างกลยุทธ์ให้เติบโตและมีกำไร อาทิเช่น การสร้างสายสัมพันธ์กับลูกค้า, ช่องทางการตลาด, สิ่งที่ต้องทำเพื่อขับเคลื่อนธุรกิจ, พาร์ทเนอร์หลักของเรา, ทรัพยากรที่จำเป็นของบริษัท, ค่าใช้จ่ายหลักของธุรกิจ และ รายได้ของธุรกิจ
สุดท้ายแล้ว เมื่อนำแนวคิดการออกแบบคุณค่าที่ครบถ้วนตามแผนภาพการสร้างคุณค่า จะพบว่าการออกแบบคุณค่าทางธุรกิจที่เหนือกว่าคู่แข่งได้นั้น คือ การระบุคุณค่าที่แม้แต่ลูกค้าเองยังไม่เคยรับรู้มาก่อน หรือยังไม่รู้ตัวด้วยซ้ำว่าต้องการสิ่งนี้ นั่นคือการค้นหาความต้องการที่ซ่อนในใจลูกค้าที่ไปไกลกว่าสิ่งที่ลูกค้าคาดหวังหรือจากประสบการณ์เดิมที่ลูกค้าได้รับจนชินนั่นเอง
เอกสารการอ้างอิง
Osterwalder, A., and Pigneur, Y. (2010), Business Model Generation,
Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.
Osterwalder, A., and Pigneur, Y., Bernarda, G., Smith, A. (2014), Value Proposition Design:
How to Create Products and Services Customers Want, Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.